


Australian Biological Resources Study
| Checklist of the Lichens of Australia and its Island Territories | ||
| Introduction | A–D | E–O | P–R | S–Z | Oceanic Islands | References | ||
| Pseudocyphellaria pickeringii (Tuck.) D.J.Galloway | ||
| Bull. Brit. Mus. (Nat. Hist.), Bot. 17: 218 (1988); Sticta pickeringii Tuck., in C.Wilkes, U.S. Expl. Exped., Bot. 17: 138 (1862). T: Bay of Islands, North Auckland, New Zealand, Wilkes Expedition; holo: FH. ***** Sticta flavissima var. simulans Müll.Arg., Bull. Herb. Boissier 4: 89 (1896). T: Qld, s. loc., F.M.Bailey 49; lecto: G 002011, fide D.J.Galloway, Bull. Brit. Mus. (Nat. Hist.), Bot. 17: 218 (1988); syn: G 002012, 002014, 002015. | ||
| Thallus rosette-forming to irregularly spreading, loosely to closely attached centrally, 5–10 (–20) cm wide. Lobes very variable, ±rounded to ragged-incised to complexly divided, to 2 cm long, 0.5–1.5 cm wide; lobe margins entire to notched or incised, becoming richly phyllidiate. Upper surface pale yellow-green to tawny when dry, emerald-green to glaucous green when wet, convex-undulate, shallowly wrinkled or pitted to ±faveolate in parts, matt or glossy, smooth or minutely scabrid-areolate in parts; lacking maculae, pseudocyphellae and soredia. Isidia mainly marginal then spreading to upper surface, minute, terete, becoming flattened-coralloid, phyllidiate. Phyllidia flattened, 0.2–3 mm tall; upper surface convex; lower surface pale yellow; margins ridged, with scattered minute yellow pseudocyphellae. Medulla yellow. Photobiont green. Lower surface yellow-white, glabrous at margins to dark red-brown and tomentose centrally. Pseudocyphellae scattered, fleck-like, yellow. Apothecia uncommon, sessile, 0.2–5 mm diam.; disc pale to dark red-brown; exciple pale whitish buff, coarsely verrucose-areolate; epithecium red-brown, K–; hymenium colourless; hypothecium red-brown or pale brick-red, K+ blue-green (deeper layers staining most strongly); zone near hymenium brownish yellow. Ascospores fusiform-ellipsoidal, 1–3 (–5)-septate, 25–32 × 6–7 µm, colourless. CHEMISTRY: Pulvinic acid, pulvinic dilactone, calycin, 2α,3β,22α-triacetoxystictane, 2α,3β-diacetoxystictane-22-ol, stictane-3β,22α-diol, 2β-acetoxystictane-3β,22α-diol, 3β-acetoxy-stictane-2α,22α-diol, stictane-2α,3β,22α-triol, 3β-acetoxystictane-22-ol, pseudocyphellarin A, isopseudocyphellarin A, nephroarctin, phenarctin, 2'-O-methylphenarctin, 1'-chloro-phenarctin, 2'-O-methylpseudocyphellarin A and 2'-O-methylisopseudocyphellarin A. | 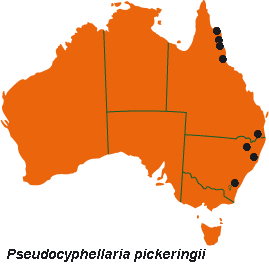 |
|
| Occurs in eastern Qld and eastern N.S.W. and in Lord Howe Is. and Norfolk Is.; grows on rock faces, living and dead wood, tree stumps and shrubs in open woodland and rainforest. Also in New Zealand and throughout the Palaeotropics. | ||
| Galloway et al. (2001) | ||
| Checklist Index |
| Introduction | A–D | E–O | P–R | S–Z | Oceanic Islands | References |
This work is copyright. Apart from any use as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, no part may be reproduced by any process without prior written permission from Australian Biological Resources Study. Requests and inquiries concerning reproduction and rights should be addressed in the first instance to Dr P. McCarthy. These pages may not be displayed on, or downloaded to, any other server without the express permission of ABRS.